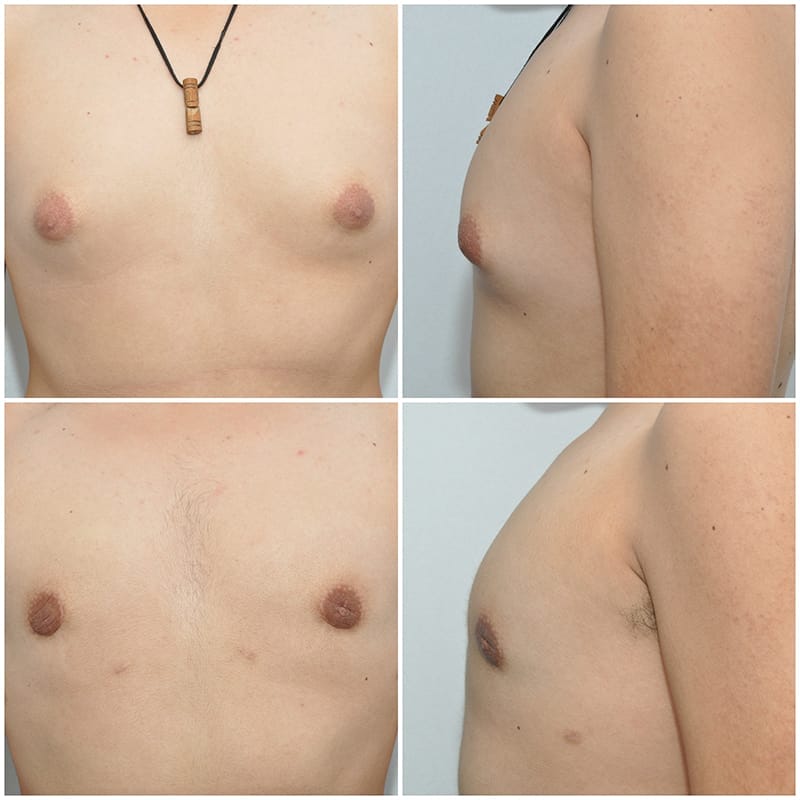
Gynecomastia is not an uncommon disorder. It can present in young males as they go through puberty and the hormone levels in the blood rise. The disorder can also be found in older male patients who have been exposed to extrinsic hormones, like testosterone or estrogen. In either case, enlargement of the male breasts occurs, causing them to resemble female breasts. This can be further exacerbated by fat accumulation on the chest, which will worsen the aesthetic situation. Cases that are not related to hormonal issues s are usually called idiopathic, which means there is no medical explanation for the development of the disorder. However, it is important that a young patient have a consultation with his pediatrician in order to rule out any hormonal imbalance he might have. Once it has been ascertained that the patient has no endocrine issues, we can proceed with surgical treatment. In a young patient who simply develops enlargement of the breasts without any component of fat surrounding or infiltrating the breasts, the indicated treatment consists of making a small incision around the areola and subsequent removal of the gland; the procedure is technically called a subcutaneous mastectomy.
The removed tissue is routinely submitted for examination by a pathologist. At the end of the surgery, the incision will be closed with resorbable sutures, and a compression vest will be used for approximately 1-2 weeks until the swelling in the area subsides, the stitches are absorbed and the wound has healed, allowing the patient to return to his normal activities. In other cases, when a fatty component is added to true gynecomastia, the treatment is different. This could be the case in a young patient who is overweight, but is usually seen in older patients. Breast tissue has a large component of fat, which can be up to 50% of the total volume, and also is spread across the entire pectoral (chest) area. A combined procedure must be done in order to avoid deformities of the chest that usually are created when the procedure is not properly done, and result in severe indentation deformities under the areolae. Ultrasonic-assisted lipectomy should be done first to remove some of the breast tissue and the fat in the area, followed by removal of the residual breast gland that we then locate under the areola, which is entered through a small incision performed in that area.
The procedure starts with infiltration of tumescent solution, the same as used for liposculpture. Two small incisions, one on each side (laterally and medially) of the subpectoral fold (i.e. where the pectoralis muscle ends), are made, and through those incisions ultrasonic liposuction is performed, removing as much breast tissue and fat as possible in order to create a smooth and flattened chest area. The residual ?lump? of dense, fibrous breast tissue will then be surgically removed through a peri-areolar incision. This part of the surgery is facilitated by the dissection that was already performed with the ultrasonic cannula, and allows the surgeon to smoothly remove the remaining portions of breast tissue, creating a smooth, regular surface at the end of the surgery. This combined approach leads to excellent results and high patient satisfaction. In cases in which ultrasonic liposuction is performed, a drain is left in place to allow for faster healing. A compression vest is also utilized. The drain is usually removed 2-3 days postoperatively. The compression vest should be maintained in place for approximately 3 weeks. Nevertheless, the patient will be ready to go back to school or work approximately 2-3 days after the surgery is performed. Finally, there are cases in which, secondary to extreme obesity, the skin in the area becomes completely stretched, so that in addition to removing the fat and the breast tissue, the excess skin needs to be addressed. These cases are more complex and require different incisions in order to remove the excess skin. The most important goal in this disorder is to achieve a smooth surface at the end of the procedure, remove the breast tissue and avoid complications that are nearly impossible to treat once they occur. If you need further information, do not hesitate to contact our practice!
- Home
- About Us
- Breast
- Body
- Face
- Tempsure Envi
- Deep Plane Facelift
- Rhinoplasty
- Ultrasonic Rhinoplasty
- Septoplasty
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Otoplasty (Ear Surgery)
- Mentoplasty (Chin Implants)
- Endoscopic Brow Lift
- Smartgraft FUE Hair Transplant
- Hair Transplant Surgery
- Non-Surgical Treatment of Alopecia
- Rhinophyma
- Dermal Fillers
- Neck Lift
- Skin
- Payment Plans
- Home
- About Us
- Breast
- Body
- Face
- Tempsure Envi
- Deep Plane Facelift
- Rhinoplasty
- Ultrasonic Rhinoplasty
- Septoplasty
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Otoplasty (Ear Surgery)
- Mentoplasty (Chin Implants)
- Endoscopic Brow Lift
- Smartgraft FUE Hair Transplant
- Hair Transplant Surgery
- Non-Surgical Treatment of Alopecia
- Rhinophyma
- Dermal Fillers
- Neck Lift
- Skin
- Payment Plans